|
A to F G to M N to T U to Z See also: - Polygon |
Triangle A triangle is a polygon which has three sides. The vertex (plural vertices) of a triangle is the point where two of it's sides meet. In general, the vertices of a triangle are labelled with upper-case letters and the sides opposite each angle with the equivalent lower-case letter. A scalene triangle is a triangle with no congruent sides (ie. all sides have different lengths). Therefore, in a scalene triangle ABC, a 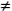 b b 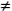 c. c.
An isosceles triangle is a triangle with two congruent sides. In an isosceles triangle ABC, a = c. The two equal sides are called the legs and the other side is called the base. The angles adjoining the base are called the base angles and the other angle (opposite the base) is called the vertex angle. An equilateral triangle is a triangle with three congruent sides. In an equilateral triangle ABC, a = b = c. An equilateral triangle is also an isosceles triangle. A right or right-angled triangle is a triangle with a right angle. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse and the two sides adjoining the right angle are called the legs or arms. An obtuse triangle is a triangle with one obtuse angle. The other two angles will therefore be acute. An acute triangle is a triangle with three acute angles. |
Top
[ H O M E ] [ S C I E N C E ] [ M A T H S ] [ A S T R O N O M Y ] [ S E A R C H ]
[ A to F ] [ G to M ] [ N to T ] [ U to Z ]
© 1997 - 1999, Jonathan Stott